|
x
|
ANNUAL
REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d)
OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF
1934
|
|
o
|
TRANSITION
REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE
ACT OF
1934
|
|
New
York
|
13-3119827
|
|
|
(State
or Other Jurisdiction
|
(I.R.S.
Employer
|
|
|
of
Incorporation or Organization)
|
Identification
No.)
|
|
111
West 57th Street, New York, New York
|
10019
|
|
(Address
of Principal Executive Offices)
|
(Zip
Code)
|
|
Title
of Each Class
|
Name
of Each Exchange on Which Registered
|
|
|
Common
Stock, $.01 par value
|
Nasdaq
Global Market
|
|
Large
Accelerated Filer ¨
|
Accelerated
Filer x
|
Non-Accelerated
Filer ¨
|
|
DOCUMENTS
INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
|
INCORPORATED
AT
|
|
|
Harris
& Harris Group, Inc. Proxy Statement for the
|
Part
III, Items 10, 11,
|
|
|
2008
Annual Meeting of Shareholders
|
12,
13 and 14
|
|
Page
|
||
|
PART
I
|
||
|
Item
1.
|
Business
|
1
|
|
Item
1A.
|
Risk
Factors
|
15
|
|
Item
1B.
|
Unresolved
Staff Comments
|
27
|
|
Item
2.
|
Properties
|
28
|
|
Item
3.
|
Legal
Proceedings
|
28
|
|
Item
4.
|
Submission
of Matters to a Vote of Security Holders
|
28
|
|
PART
II
|
||
|
Item
5.
|
Market
For Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer
Purchases of Equity Securities
|
29
|
|
Item
6.
|
Selected
Financial Data
|
32
|
|
Item
7.
|
Management's
Discussion and Analysis of Financial
|
|
|
Condition
and Results of Operations
|
33
|
|
|
Item
7A.
|
Quantitative
and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
|
49
|
|
Item
8.
|
Consolidated
Financial Statements and
Supplementary Data
|
51
|
|
Item
9.
|
Changes
in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial
Disclosure
|
104
|
|
Item
9A.
|
Controls
and Procedures
|
104
|
|
Item
9B.
|
Other
Information
|
104
|
|
PART
III
|
||
|
Item
10.
|
Directors
and Executive Officers of the Registrant
|
105
|
|
Item
11.
|
Executive
Compensation
|
105
|
|
Item
12.
|
Security
Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related
Stockholder Matters
|
105
|
|
Item
13.
|
Certain
Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director
Independence
|
105
|
|
Item
14.
|
Principal
Accountant Fees and Services
|
106
|
|
PART
IV
|
||
|
Item
15.
|
Exhibits
and Financial Statements Schedules
|
107
|
|
Signatures
|
110
|
|
|
Exhibit Index
|
112
|
| · |
Equity,
equity-related securities (including warrants) and debt with equity
features from either private or public
issuers;
|
| · |
Venture
capital investments, whether in corporate, partnership or other form,
including development stage or start-up
entities;
|
| · |
Intellectual
property or patents or research and development in technology or
product
development that may lead to patents or other marketable
technology;
|
| · |
Debt
obligations of all types having varying terms with respect to security
or
credit support, subordination, purchase price, interest payments
and
maturity;
|
| · |
Foreign
securities; and
|
| · |
Miscellaneous
investments.
|
| · |
recruiting
management;
|
| · |
formulating
operating strategies;
|
| · |
formulating
intellectual property strategies;
|
| · |
assisting
in financial planning;
|
| · |
providing
management in the initial start-up stages; and
|
| · |
establishing
corporate goals.
|
| · |
funding
research and development in the development of a technology;
|
| · |
obtaining
licensing rights to intellectual property or patents;
|
| · |
acquiring
intellectual property or patents;
or
|
| · |
forming
and funding companies or joint ventures to commercialize further
intellectual property.
|
| • |
stock
market and capital markets
conditions;
|
| • |
internal
developments in our Company with respect to our personnel, financial
condition
and compliance with all applicable
regulations;
|
| • |
announcements
regarding any of our portfolio
companies;
|
| • |
announcements
regarding developments in the nanotechnology field in
general;
|
| • |
environmental
and health concerns regarding nanotechnology, whether real or perceptual;
|
| • |
announcements
regarding government funding and initiatives related to the development
of nanotechnology;
|
| • |
general
economic conditions and trends;
and/or
|
| • |
departures
of key personnel.
|
| Item 5. |
Market
for Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and
Issuer Purchases of Equity
Securities.
|
|
2007
Quarter Ending
|
Low
|
|
High
|
|
|||
|
March
31
|
$
|
11.00
|
$
|
13.58
|
|||
|
June
30
|
$
|
11.01
|
$
|
14.32
|
|||
|
September
30
|
$
|
9.51
|
$
|
11.79
|
|||
|
December
31
|
$
|
8.00
|
$
|
11.10
|
|||
|
2006
Quarter Ending
|
|
Low
|
High
|
||||
|
March
31
|
$
|
12.75
|
$
|
16.10
|
|||
|
June
30
|
$
|
9.57
|
$
|
14.26
|
|||
|
September
30
|
$
|
9.38
|
$
|
12.99
|
|||
|
December
31
|
$
|
11.80
|
$
|
15.16
|
|||
|
EQUITY
COMPENSATION PLAN INFORMATION
As
of December 31, 2007
|
|
|
Number
of securities
to
be issued upon
exercise
of out-
standing
options,
warrants
and rights
|
Weighted-average
exercise
price of
outstanding
options,
warrants
and rights
|
Number
of securities
remaining available for
future
issuance under
equity
compensation
plans
(excluding
securities
reflected in
Column
(a))
|
|||||||
|
Plan
category
|
(a)
|
|
(b)
|
|
(c)
|
|
||||
|
Equity
compensation plans approved by security holders
|
3,967,744
|
$
|
10.54
|
(1)
|
|
|||||
|
Equity
compensation plans not approved by security holders
|
||||||||||
|
TOTAL
|
3,967,744
|
$
|
10.54
|
(1)
|
|
|||||

|
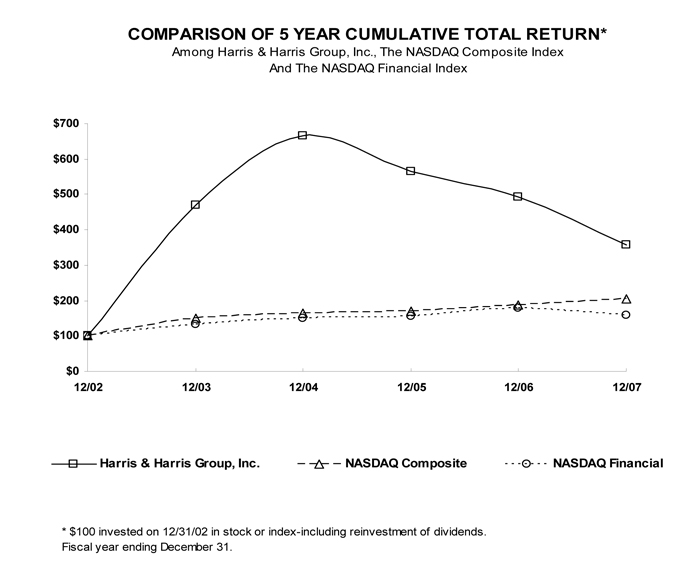
|
12/02
|
12/03
|
12/04
|
12/05
|
12/06
|
12/07
|
|||||||||||||
|
Harris
& Harris Group, Inc.
|
100.00
|
468.70
|
665.85
|
565.04
|
491.46
|
357.32
|
|||||||||||||
|
NASDAQ
Composite
|
100.00
|
149.75
|
164.64
|
168.60
|
187.83
|
205.22
|
|||||||||||||
|
NASDAQ
Financial
|
100.00
|
133.86
|
149.89
|
156.52
|
178.54
|
157.20
|
|||||||||||||
|
2007
|
2006
|
2005
|
2004
|
2003
|
||||||||||||
|
Total
assets
|
$
|
142,893,332
|
$
|
118,328,590
|
$
|
132,938,120
|
$
|
79,361,451
|
$
|
44,115,128
|
||||||
|
Total
liabilities
|
$
|
4,529,988
|
$
|
4,398,287
|
$
|
14,950,378
|
$
|
4,616,652
|
$
|
3,432,390
|
||||||
|
Net
assets
|
$
|
138,363,344
|
$
|
113,930,303
|
$
|
117,987,742
|
$
|
74,744,799
|
$
|
40,682,738
|
||||||
|
Net
asset value per outstanding share
|
$
|
5.93
|
$
|
5.42
|
$
|
5.68
|
$
|
4.33
|
$
|
2.95
|
||||||
|
Cash
dividends paid
|
$
|
0.00
|
$
|
0.00
|
$
|
0.00
|
$
|
0.00
|
$
|
0.00
|
||||||
|
Cash
dividends paid per outstanding share
|
$
|
0.00
|
$
|
0.00
|
$
|
0.00
|
$
|
0.00
|
$
|
0.00
|
||||||
|
Shares
outstanding, end of year
|
23,314,573
|
21,015,017
|
20,756,345
|
17,248,845
|
13,798,845
|
|||||||||||
|
2007
|
2006
|
2005
|
2004
|
2003
|
||||||||||||
|
Total
investment income
|
$
|
2,705,636
|
$
|
3,028,761
|
$
|
1,540,862
|
$
|
637,562
|
$
|
167,785
|
||||||
|
Total
expenses1
|
$
|
14,533,179
|
$
|
10,641,696
|
$
|
7,006,623
|
$
|
4,046,341
|
$
|
2,731,527
|
||||||
|
Net
operating (loss) income
|
$
|
(11,827,543
|
)
|
$
|
(7,612,935
|
)
|
$
|
(5,465,761
|
)
|
$
|
(3,408,779
|
)
|
$
|
(2,563,742
|
) | |
|
Total
tax (benefit) expense2
|
$
|
87,975
|
$
|
(227,355
|
)
|
$
|
8,288,778
|
$
|
650,617
|
$
|
13,761
|
|||||
|
Net
realized income (loss) from investments
|
$
|
30,162
|
$
|
258,693
|
$
|
14,208,789
|
$
|
858,503
|
$
|
(984,925
|
)
|
|||||
|
Net
decrease (increase) in unrealized depreciation on
investments
|
$
|
5,080,936
|
$
|
(4,418,870
|
)
|
$
|
(2,026,652
|
)
|
$
|
484,162
|
$
|
343,397
|
||||
|
Net
(decrease) increase in net assets resulting from
operations
|
$
|
(6,716,445
|
)
|
$
|
(11,773,112
|
)
|
$
|
6,716,376
|
$
|
(2,066,114
|
)
|
$
|
(3,205,270
|
)
|
||
|
(Decrease)
increase in net assets resulting from operations per average
outstanding
share
|
$
|
(0.30
|
)
|
$
|
(0.57
|
)
|
$
|
0.36
|
$
|
(0.13
|
)
|
$
|
(0.28
|
)
|
||
| Item 7. |
Management's
Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and
Results of Operations.
|
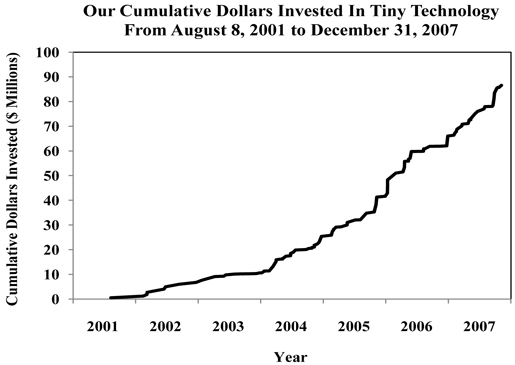
|
2001
|
2002
|
2003
|
2004
|
2005
|
2006
|
2007
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Total
Incremental Investments
|
$
|
489,999
|
$
|
6,240,118
|
$
|
3,812,600
|
$
|
14,837,846
|
$
|
16,251,339
|
$
|
24,408,187
|
$
|
20,595,161
|
||||||||
|
No.
of New Investments
|
1
|
7
|
5
|
8
|
4
|
6
|
7
|
|||||||||||||||
|
No.
of Follow-On Investment Rounds
|
0
|
1
|
5
|
21
|
13
|
14
|
20
|
|||||||||||||||
|
No.
of Rounds Led
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
2
|
0
|
7
|
3
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Average
Dollar Amount –
Initial
|
$
|
489,999
|
$
|
784,303
|
$
|
437,156
|
$
|
911,625
|
$
|
1,575,000
|
$
|
2,383,424
|
$
|
1,086,441
|
||||||||
|
Average
Dollar Amount – Follow- On
|
N/A
|
$
|
750,000
|
$
|
325,364
|
$
|
359,278
|
$
|
765,488
|
$
|
721,974
|
$
|
649,504
|
|||||||||
|
2001
|
2002
|
2003
|
2004
|
2005
|
2006
|
2007
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Net
Asset Value, BOY
|
$
|
31,833,475
|
$
|
24,334,770
|
$
|
27,256,046
|
$
|
40,682,738
|
$
|
74,744,799
|
$
|
117,987,742
|
$
|
113,930,303
|
||||||||
|
Gross
Write-Downs During Year
|
$
|
(2,532,730
|
)
|
$
|
(5,400,005
|
)
|
$
|
(1,256,102
|
)
|
$
|
(5,711,229
|
)
|
$
|
(3,450,236
|
)
|
$
|
(4,211,323
|
)
|
$
|
(7,810,794
|
)
|
|
|
Gross
Write-Ups During Year
|
$
|
1,528,866
|
$
|
285
|
$
|
847,578
|
$
|
6,288,397
|
$
|
23,485,176
|
$
|
279,363
|
$
|
11,694,618
|
||||||||
|
Gross
Write-Downs as a Percentage of Net Asset Value, BOY
|
-7.96
|
%
|
-22.19
|
%
|
-4.61
|
%
|
-14.04
|
%
|
-4.62
|
%
|
-3.57
|
%
|
-6.86
|
%
|
||||||||
|
Gross
Write-Ups as a Percentage of Net Asset Value, BOY
|
4.80
|
%
|
0
|
%
|
3.11
|
%
|
15.46
|
%
|
31.42
|
%
|
0.24
|
%
|
10.26
|
%
|
||||||||
|
Net
Write-Downs/Write-Ups as a Percentage of Net Asset Value,
BOY
|
-3.15
|
%
|
-22.19
|
%
|
-1.49
|
%
|
1.42
|
%
|
26.8
|
%
|
-3.33
|
%
|
3.40
|
%
|
||||||||
|
New
Investments
|
Cost
|
|||
|
Adesto
Technologies Corporation
|
$
|
1,147,826
|
||
|
Ancora
Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
|
$
|
800,000
|
||
|
BioVex
Group, Inc.
|
$
|
2,500,000
|
||
|
Ensemble
Discovery Corporation
|
$
|
2,000,000
|
||
|
Lifco,
Inc.
|
$
|
946,528
|
||
|
Phoenix
Molecular Corporation
|
$
|
50,010
|
||
|
Siluria
Technologies, Inc.
|
$
|
160,723
|
||
|
Follow-on
Investments
|
||||
|
BridgeLux,
Inc.
|
$
|
350,877
|
||
|
BridgeLux,
Inc.
|
$
|
233,918
|
||
|
BridgeLux,
Inc.
|
$
|
916,928
|
||
|
Cambrios
Technologies Corporation
|
$
|
1,300,000
|
||
|
Chlorogen,
Inc.
|
$
|
7,042
|
||
|
CSwitch,
Inc.
|
$
|
32,624
|
||
|
CSwitch,
Inc.
|
$
|
529,852
|
||
|
Innovalight,
Inc.
|
$
|
1,993,568
|
||
|
Kereos,
Inc.
|
$
|
540,000
|
||
|
Kovio,
Inc.
|
$
|
1,000,000
|
||
|
NanoGram
Corporation
|
$
|
851,393
|
||
|
Mersana
Therapeutics, Inc.
|
$
|
500,000
|
||
|
Nanomix,
Inc.
|
$
|
680,240
|
||
|
NanoOpto
Corporation
|
$
|
268,654
|
||
|
Nextreme
Thermal Solutions, Inc.
|
$
|
750,000
|
||
|
Polatis,
Inc.
|
$
|
17,942
|
||
|
Polatis,
Inc.
|
$
|
13,454
|
||
|
Polatis,
Inc.
|
$
|
58,582
|
||
|
SiOnyx,
Inc.
|
$
|
2,445,000
|
||
|
Solazyme,
Inc.
|
$
|
500,000
|
||
|
Total
|
$
|
20,595,161
|
|
December
31,
|
|||||||
|
2007
|
2006
|
||||||
|
Venture
capital investments, at cost
|
$
|
82,677,528
|
$
|
62,118,800
|
|||
|
Net
unrealized depreciation (1)
|
4,567,144
|
8,450,969
|
|||||
|
Venture
capital investments, at value
|
$
|
78,110,384
|
$
|
53,667,831
|
|||
|
December
31,
|
|||||||
|
2007
|
2006
|
||||||
|
U.S.
government and agency obligations, at cost
|
$
|
59,552,933
|
$
|
59,212,598
|
|||
|
Net
unrealized appreciation (depreciation) (1)
|
640,660
|
(556,451
|
)
|
||||
|
U.S.
government and agency obligations, at value
|
$
|
60,193,593
|
$
|
58,656,147
|
|||
|
December
31,
|
|||||||
|
Category
|
2007
|
2006
|
|||||
|
Tiny
Technology
|
99.9
|
%
|
99.9
|
%
|
|||
|
Other
Venture Capital Investments
|
0.1
|
%
|
0.1
|
%
|
|||
|
Total
Venture Capital Investments
|
100.0
|
%
|
100.0
|
%
|
|||
|
New
Investments
|
Cost
|
|||
|
D-Wave
Systems, Inc.
|
$
|
1,750,547
|
||
|
Evolved
Nanomaterial Sciences, Inc.
|
2,800,000
|
|||
|
Innovalight,
Inc.
|
2,500,000
|
|||
|
Metabolon,
Inc.
|
2,500,000
|
|||
|
SiOnyx,
Inc.
|
750,000
|
|||
|
Xradia,
Inc.
|
4,000,000
|
|||
|
Follow-on
Investments
|
||||
|
Chlorogen,
Inc.
|
$
|
221,438
|
||
|
Crystal
IS, Inc.
|
1,098,240
|
|||
|
CSwitch
Corporation
|
2,850,000
|
|||
|
NanoGram
Corporation
|
1,262,764
|
|||
|
NanoOpto
Corporation
|
433,138
|
|||
|
NeoPhotonics
Corporation
|
2,750,000
|
|||
|
Nextreme
|
500,000
|
|||
|
Polatis,
Inc.
|
89,310
|
|||
|
Questech
Corporation
|
12,750
|
|||
|
SiOnyx,
Inc.
|
890,000
|
|||
|
Total
|
$
|
24,408,187
|
|
Documents
|
Page
|
|
|
52
|
||
|
Report
of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
|
53
|
|
|
Consolidated
Financial Statements
|
||
|
Consolidated
Statements of Assets and Liabilities as of December 31, 2007, and
2006
|
55
|
|
|
Consolidated
Statements of Operations for the years ended December 31, 2007,
2006,
2005
|
56
|
|
|
Consolidated
Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2007,
2006, and
2005
|
57
|
|
|
Consolidated
Statements of Changes in Net Assets for the years ended December
31, 2007,
2006, and 2005
|
58
|
|
|
|
||
|
Consolidated
Schedule of Investments as of December 31, 2007
|
59-69
|
|
|
Consolidated
Schedule of Investments as of December 31, 2006
|
70-77
|
|
|
Footnote
to Consolidated Schedule of Investments
|
78-82
|
|
|
Notes
to Consolidated Financial Statements
|
83-102
|
|
|
103
|
|
•
|
pertain
to the maintenance of records that in reasonable detail accurately
and
fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of
the
Company;
|
|
•
|
provide
reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary
to permit
preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally
accepted
accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the
company
are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management
and
directors of the Company; and
|
|
•
|
provide
reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of
unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the Company's assets
that
could have a material effect on the financial
statements.
|
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED
STATEMENTS OF ASSETS AND
LIABILITIES
|
|
December 31, 2007
|
December 31, 2006
|
||||||
|
ASSETS
|
|||||||
|
Investments,
at value (Cost: $142,230,461 at 12/31/07, $121,331,398 at
12/31/06)
|
$
|
138,303,977
|
$
|
112,323,978
|
|||
|
Cash
and cash equivalents
|
330,009
|
2,071,788
|
|||||
|
Restricted
funds (Note 7)
|
2,667,020
|
2,149,785
|
|||||
|
Receivable
from portfolio company
|
524
|
0
|
|||||
|
Receivable
from broker (Note 4)
|
0
|
819,905
|
|||||
|
Interest
receivable
|
647,337
|
625,372
|
|||||
|
Prepaid
expenses
|
488,667
|
10,945
|
|||||
|
Other
assets
|
455,798
|
326,817
|
|||||
|
Total
assets
|
$
|
142,893,332
|
$
|
118,328,590
|
|||
|
LIABILITIES
& NET ASSETS
|
|||||||
|
Accounts
payable and accrued liabilities (Note 7)
|
$
|
4,515,463
|
$
|
4,115,300
|
|||
|
Accrued
profit sharing (Note 5)
|
0
|
261,661
|
|||||
|
Deferred
rent
|
14,525
|
21,326
|
|||||
|
Total
liabilities
|
4,529,988
|
4,398,287
|
|||||
|
Net
assets
|
$
|
138,363,344
|
$
|
113,930,303
|
|||
|
Net
assets are comprised of:
|
|||||||
|
Preferred
stock, $0.10 par value, 2,000,000 shares authorized; none
issued
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
$
|
0
|
|
|
Common
stock, $0.01 par value, 45,000,000 shares authorized at 12/31/07
and
12/31/06; 25,143,313 issued at 12/31/07 and 22,843,757 issued at
12/31/06
|
|
|
251,434
|
|
|
228,438
|
|
|
Additional
paid in capital (Note 10)
|
160,927,691
|
129,801,201
|
|||||
|
Accumulated
net realized loss
|
(15,483,766
|
)
|
(3,686,385
|
)
|
|||
|
Accumulated
unrealized depreciation of investments
|
(3,926,484
|
)
|
(9,007,420
|
)
|
|||
|
Treasury
stock, at cost (1,828,740 shares at 12/31/07 and 12/31/06)
|
(3,405,531
|
)
|
(3,405,531
|
)
|
|||
|
Net
assets
|
$
|
138,363,344
|
$
|
113,930,303
|
|||
|
Shares
outstanding
|
23,314,573
|
21,015,017
|
|||||
|
Net
asset value per outstanding share
|
$
|
5.93
|
$
|
5.42
|
|||
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED
STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
|
|
Year Ended
|
Year Ended
|
Year Ended
|
||||||||
|
December 31, 2007
|
December 31, 2006
|
December 31, 2005
|
||||||||
|
Investment
income:
|
||||||||||
|
Interest
from:
|
||||||||||
|
Fixed-income
securities
|
$
|
2,705,597
|
$
|
2,991,261
|
$
|
1,409,273
|
||||
|
Portfolio
companies
|
0
|
0
|
65,620
|
|||||||
|
Miscellaneous
income
|
39
|
37,500
|
65,969
|
|||||||
|
Total
investment income
|
2,705,636
|
3,028,761
|
1,540,862
|
|||||||
|
Expenses:
|
||||||||||
|
Salaries,
benefits and stock-based compensation (Note 4)
|
11,435,329
|
7,933,276
|
2,459,033
|
|||||||
|
Administration
and operations
|
1,432,653
|
1,250,080
|
1,319,354
|
|||||||
|
Profit-sharing
provision (Note 5)
|
0
|
50,875
|
1,796,264
|
|||||||
|
Professional
fees
|
902,911
|
737,828
|
830,062
|
|||||||
|
Rent
|
235,998
|
239,846
|
211,582
|
|||||||
|
Directors'
fees and expenses
|
435,060
|
340,750
|
308,874
|
|||||||
|
Depreciation
|
63,113
|
64,916
|
64,713
|
|||||||
|
Custodian
fees
|
28,115
|
24,125
|
16,741
|
|||||||
|
Total
expenses
|
14,533,179
|
10,641,696
|
7,006,623
|
|||||||
|
Net
operating loss
|
(11,827,543
|
)
|
(7,612,935
|
)
|
(5,465,761
|
)
|
||||
|
Net
realized gain from investments:
|
||||||||||
|
Realized
gain from investments
|
118,137
|
31,338
|
23,862,037
|
|||||||
|
Income
tax expense (benefit) (Note 8)
|
87,975
|
(227,355
|
)
|
9,653,248
|
||||||
|
Net
realized gain from investments
|
30,162
|
258,693
|
14,208,789
|
|||||||
|
Net
decrease (increase) in unrealized depreciation on
investments:
|
||||||||||
|
Change
as a result of investment sales
|
0
|
0
|
(23,181,420
|
)
|
||||||
|
Change
on investments held
|
5,080,936
|
(4,418,870
|
)
|
19,790,298
|
||||||
|
Change
in unrealized depreciation on investments
|
5,080,936
|
(4,418,870
|
)
|
(3,391,122
|
)
|
|||||
|
Income
tax (benefit) (Note 8)
|
0
|
0
|
(1,364,470
|
)
|
||||||
|
Net
decrease (increase) in unrealized depreciation on
investments
|
5,080,936
|
(4,418,870
|
)
|
(2,026,652
|
)
|
|||||
|
Net
(decrease) increase in net assets resulting from
operations:
|
||||||||||
|
Total
|
$
|
(6,716,445
|
)
|
$
|
(11,773,112
|
)
|
$
|
6,716,376
|
||
|
Per
average basic and diluted outstanding share
|
$
|
(0.30
|
)
|
$
|
(0.57
|
)
|
$
|
0.36
|
||
|
Average
outstanding shares
|
22,393,030
|
20,759,547
|
18,471,770
|
|||||||
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED
STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
|
|
Year Ended
|
Year Ended
|
Year Ended
|
||||||||
|
December 31, 2007
|
December 31, 2006
|
December 31, 2005
|
||||||||
|
Cash
flows used in operating activities:
|
||||||||||
|
Net
(decrease) increase in net assets resulting from
operations
|
$
|
(6,716,445
|
)
|
$
|
(11,773,112
|
)
|
$
|
6,716,376
|
||
|
Adjustments
to reconcile net increase (decrease) in net assets resulting from
operations to net cash used in operating activities:
|
||||||||||
|
Net
realized and unrealized (gain) loss on investments
|
(5,199,073
|
)
|
4,420,619
|
(20,470,915
|
)
|
|||||
|
Deferred
income taxes
|
0
|
0
|
(1,364,470
|
)
|
||||||
|
Depreciation
and amortization
|
(60,009
|
)
|
(426,168
|
)
|
346,019
|
|||||
|
Taxes
payable on behalf of shareholders on deemed dividend
|
0
|
0
|
8,122,367
|
|||||||
|
Stock-based
compensation expense
|
8,050,807
|
5,038,956
|
0
|
|||||||
|
Changes
in assets and liabilities:
|
||||||||||
|
Restricted
funds
|
(517,235
|
)
|
(419,351
|
)
|
(138,463
|
)
|
||||
|
Receivable
from portfolio company
|
(524
|
)
|
75,000
|
(65,000
|
)
|
|||||
|
Interest
receivable
|
(21,965
|
)
|
(376,808
|
)
|
(189,603
|
)
|
||||
|
Income
tax receivable
|
0
|
0
|
(7,023
|
)
|
||||||
|
Prepaid
expenses
|
(477,722
|
)
|
(7,951
|
)
|
539,496
|
|||||
|
Other
receivables
|
819,905
|
(819,905
|
)
|
0
|
||||||
|
Other
assets
|
(152,012
|
)
|
(176,325
|
)
|
11,599
|
|||||
|
Accounts
payable and accrued liabilities
|
400,163
|
1,002,643
|
268,525
|
|||||||
|
Accrued
profit sharing
|
(261,661
|
)
|
(1,846,197
|
)
|
1,796,264
|
|||||
|
Deferred
rent
|
(6,801
|
)
|
(9,677
|
)
|
(3,927
|
)
|
||||
|
Current
income tax liability
|
0
|
(9,637,026
|
)
|
1,524,470
|
||||||
|
Net
cash used in operating activities
|
(4,142,572
|
)
|
(14,955,302
|
)
|
(2,914,285
|
)
|
||||
|
Cash
flows from investing activities:
|
||||||||||
|
Net
(purchase) sale of short-term investments and marketable
securities
|
(235,754
|
)
|
37,593,589
|
(52,144,482
|
)
|
|||||
|
Investment
in private placements and loans
|
(20,595,161
|
)
|
(24,408,187
|
)
|
(16,251,339
|
)
|
||||
|
Proceeds
from sale of investments
|
174,669
|
28,295
|
35,392,200
|
|||||||
|
Purchase
of fixed assets
|
(41,640
|
)
|
(15,086
|
)
|
(45,704
|
)
|
||||
|
Net
cash (used in) provided by investing activities
|
(20,697,886
|
)
|
13,198,611
|
(33,049,325
|
)
|
|||||
|
Cash
flows from financing activities:
|
||||||||||
|
Proceeds
from public offering, net (Note 10)
|
12,993,168
|
0
|
36,526,567
|
|||||||
|
Proceeds
from stock option exercises (Note 4)
|
10,105,511
|
2,615,190
|
0
|
|||||||
|
Net
cash provided by financing activities
|
23,098,679
|
2,615,190
|
36,526,567
|
|||||||
|
Net
(decrease) increase in cash and cash equivalents:
|
||||||||||
|
Cash
and cash equivalents at beginning of the year
|
2,071,788
|
1,213,289
|
650,332
|
|||||||
|
Cash
and cash equivalents at end of the year
|
330,009
|
2,071,788
|
1,213,289
|
|||||||
|
Net
(decrease) increase in cash and cash equivalents
|
$
|
(1,741,779
|
)
|
$
|
858,499
|
$
|
562,957
|
|||
|
Supplemental
disclosures of cash flow information:
|
||||||||||
|
Income
taxes paid
|
$
|
80,236
|
$
|
9,425,922
|
$
|
0
|
||||
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED
STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN NET ASSETS
|
|
Year Ended
|
Year Ended
|
Year Ended
|
||||||||
|
December 31, 2007
|
December 31, 2006
|
December 31, 2005
|
||||||||
|
Changes
in net assets from operations:
|
||||||||||
|
Net
operating loss
|
$
|
(11,827,543
|
)
|
$
|
(7,612,935
|
)
|
$
|
(5,465,761
|
)
|
|
|
Net
realized gain on investments
|
30,162
|
258,693
|
14,208,789
|
|||||||
|
Net
(increase) in unrealized depreciation on investments as a result
of
sales
|
0
|
0
|
(23,181,420
|
)
|
||||||
|
Net
decrease (increase) in unrealized depreciation on investments
held
|
5,080,936
|
(4,418,870
|
)
|
19,790,298
|
||||||
|
Net
change in deferred taxes
|
0
|
0
|
1,364,470
|
|||||||
|
Net
(decrease) increase in net assets resulting from
operations
|
(6,716,445
|
)
|
(11,773,112
|
)
|
6,716,376
|
|||||
|
Changes
in net assets from capital stock transactions:
|
||||||||||
|
Issuance
of common stock upon the exercise of stock options
|
9,996
|
2,587
|
0
|
|||||||
|
Issuance
of common stock on offering
|
13,000
|
0
|
35,075
|
|||||||
|
Additional
paid in capital on common stock issued
|
23,075,683
|
2,612,603
|
36,491,492
|
|||||||
|
Stock-based
compensation expense
|
8,050,807
|
5,038,956
|
0
|
|||||||
|
Net
increase in net assets resulting from capital stock
transactions
|
31,149,486
|
7,654,146
|
36,526,567
|
|||||||
|
Changes
in net assets from adoption of SFAS No. 158
|
0
|
61,527
|
0
|
|||||||
|
Net
increase (decrease) in net assets
|
24,433,041
|
(4,057,439
|
)
|
43,242,943
|
||||||
|
Net
Assets:
|
||||||||||
|
Beginning
of the year
|
113,930,303
|
117,987,742
|
74,744,799
|
|||||||
|
End
of the year
|
$
|
138,363,344
|
$
|
113,930,303
|
$
|
117,987,742
|
||||
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED
SCHEDULE OF INVESTMENTS AS OF DECEMBER 31,
2007
|
|
Method
of
|
Shares/
|
|||||||||
|
Valuation
(1)
|
Principal
|
Value
|
||||||||
|
Investments
in Unaffiliated Companies (2)(3) – 15.25% of net assets at
value
|
||||||||||
|
Private
Placement Portfolio (Illiquid) – 15.25% of net assets at
value
|
||||||||||
|
BioVex
Group, Inc. (4)(5)(6)(7)(8) – Developing novel biologics for
treatment of cancer and infectious disease Series
E
Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
2,799,552
|
$
|
2,500,000
|
|||||
|
Exponential
Business Development Company (4)(5) — Venture capital partnership focused
on early stage companies
Limited
Partnership Interest
|
(B)
|
|
1
|
2,026
|
||||||
|
Molecular
Imprints, Inc. (4)(5) — Manufacturing nanoimprint lithography capital
equipment
|
||||||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
1,333,333
|
2,000,000
|
||||||
|
Series
C Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
1,250,000
|
2,389,250
|
||||||
|
Warrants
at $2.00 expiring 12/31/11
|
(B)
|
|
125,000
|
110,750
|
||||||
|
4,500,000
|
||||||||||
|
Nanosys,
Inc. (4)(5)(7) — Developing zero and one-dimensional inorganic
nanometer-scale materials and devices
|
||||||||||
|
Series
C Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
803,428
|
2,370,113
|
||||||
|
Series
D Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
1,016,950
|
3,000,003
|
||||||
|
5,370,116
|
||||||||||
|
Nantero,
Inc. (4)(5)(7) — Developing a high-density, nonvolatile, random access
memory chip, enabled by carbon nanotubes
|
||||||||||
|
Series
A Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
345,070
|
1,046,908
|
||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
207,051
|
628,172
|
||||||
|
Series
C Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
188,315
|
571,329
|
||||||
|
2,246,409
|
||||||||||
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED
SCHEDULE OF INVESTMENTS AS OF DECEMBER
31, 2007
|
|
Method
of
|
Shares/
|
|||||||||
|
Valuation
(1)
|
Principal
|
Value
|
||||||||
|
Investments
in Unaffiliated Companies (2)(3) – 15.25% of net assets at value
(cont.)
|
||||||||||
|
Private
Placement Portfolio (Illiquid) – 15.25% of net assets at value
(cont.)
|
||||||||||
|
NeoPhotonics
Corporation (4)(5) — Developing and manufacturing optical devices and
components
|
||||||||||
|
Common
Stock
|
(B)
|
|
716,195
|
$
|
133,141
|
|||||
|
Series
1 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
1,831,256
|
1,831,256
|
||||||
|
Series
2 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
741,898
|
741,898
|
||||||
|
Series
3 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
2,750,000
|
2,750,000
|
||||||
|
Warrants
at $0.15 expiring 01/26/10
|
(B)
|
|
16,364
|
1,325
|
||||||
|
Warrants
at $0.15 expiring 12/05/10
|
(B)
|
|
14,063
|
1,139
|
||||||
|
|
5,458,759
|
|||||||||
|
Polatis,
Inc. (4)(5)(7)(9) — Developing MEMS-based optical networking
components
|
||||||||||
|
Series
A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
16,775
|
0
|
||||||
|
Series
A-2 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
71,611
|
132,653
|
||||||
|
Series
A-4 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
4,774
|
8,768
|
||||||
|
Series
A-5 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
16,438
|
135,105
|
||||||
|
276,526
|
||||||||||
|
Starfire
Systems, Inc. (4)(5)(7) — Producing ceramic-forming
polymers
|
||||||||||
|
Common
Stock
|
(B)
|
|
375,000
|
150,000
|
||||||
|
Series
A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
600,000
|
600,000
|
||||||
|
750,000
|
||||||||||
|
Total
Unaffiliated Private Placement Portfolio (cost:
$21,435,392)
|
$
|
21,103,836
|
||||||||
|
Total
Investments in Unaffiliated Companies (cost:
$21,435,392)
|
$
|
21,103,836
|
||||||||
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED
SCHEDULE OF INVESTMENTS AS OF DECEMBER
31, 2007
|
|
Method
of
|
Shares/
|
|||||||||
|
Valuation
(1)
|
Principal
|
Value
|
||||||||
|
Investments
in Non-Controlled Affiliated Companies (2)(10) – 38.06% of net assets
at value
|
||||||||||
|
Private
Placement Portfolio (Illiquid) – 38.06% of net assets at
value
|
||||||||||
|
Adesto
Technologies Corporation (4)(5)(6)(7) — Developing semiconductor-related
products enabled at the nanoscale
|
||||||||||
|
Series
A Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
3,416,149
|
$
|
1,147,826
|
|||||
|
Ancora
Pharmaceuticals Inc. (4)(5)(6)(7) – Developing synthetic
carbohydrates for pharmaceutical markets and for internal drug
development programs
|
||||||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
909,091
|
639,062
|
||||||
|
Warrants
at $1.06 expiring 05/01/08
|
(B)
|
|
754,717
|
60,377
|
||||||
|
699,439
|
||||||||||
|
BridgeLux,
Inc. (4)(5)(11) — Manufacturing high-power light emitting
diodes
|
||||||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
1,861,504
|
2,792,256
|
||||||
|
Series
C Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
2,130,699
|
3,196,050
|
||||||
|
Warrants
at $0.7136 expiring 02/02/2017
|
(B)
|
|
98,340
|
138,856
|
||||||
|
Warrants
at $0.7136 expiring 04/26/2017
|
(B)
|
|
65,560
|
92,833
|
||||||
|
6,219,995
|
||||||||||
|
Cambrios
Technologies Corporation (4)(5)(7) — Developing nanowire-enabled
electronic materials for the display industry
|
||||||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
1,294,025
|
1,294,025
|
||||||
|
Series
C Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
1,300,000
|
1,300,000
|
||||||
|
2,594,025
|
||||||||||
|
Chlorogen,
Inc. (4)(5)(12) — Developed patented chloroplast technology to produce
plant-made proteins
|
||||||||||
|
Series
A Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
4,478,038
|
0
|
||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
2,077,930
|
0
|
||||||
|
Secured
Convertible Bridge Note (including interest)
|
(B)
|
|
$
|
176,811
|
0
|
|||||
|
0
|
||||||||||
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED
SCHEDULE OF INVESTMENTS AS OF DECEMBER
31, 2007
|
|
Method
of
|
Shares/
|
|||||||||
|
Valuation
(1)
|
Principal
|
Value
|
||||||||
|
Investments
in Non-Controlled Affiliated Companies (2)(10) – 38.06% of net assets
at value (cont.)
|
||||||||||
|
Private
Placement Portfolio (Illiquid) – 38.06% of net assets at value
(cont.)
|
||||||||||
|
Crystal
IS, Inc. (4)(5)(7) — Developing single-crystal aluminum nitride substrates
for optoelectronic devices
|
||||||||||
|
Series
A Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
391,571
|
$
|
305,425
|
|||||
|
Series
A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
1,300,376
|
1,014,294
|
||||||
|
Warrants
at $0.78 expiring 05/05/2013
|
(B)
|
|
15,231
|
9,550
|
||||||
|
Warrants
at $0.78 expiring 05/12/2013
|
(B)
|
|
2,350
|
1,473
|
||||||
|
Warrants
at $0.78 expiring 08/08/2013
|
(B)
|
|
4,396
|
2,796
|
||||||
|
1,333,538
|
||||||||||
|
CSwitch,
Inc. (4)(5)(7)(13) — Developing next-generation, system-on- a-chip
solutions for communications-based platforms
|
||||||||||
|
Series
A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
6,863,118
|
3,431,559
|
||||||
|
Secured
Convertible Bridge Note (including interest)
|
(B)
|
|
$
|
529,852
|
541,581
|
|||||
|
3,973,140
|
||||||||||
|
D-Wave
Systems, Inc. (4)(5)(7)(14) — Developing high- performance quantum
computing systems
|
||||||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
2,000,000
|
2,226,488
|
||||||
|
Ensemble
Discovery Corporation (4)(5)(6)(7) – Developing DNA Programmed
Chemistry for the discovery of new classes of therapeutics and
bioassays
|
||||||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
1,449,275
|
2,000,000
|
||||||
|
Innovalight,
Inc. (4)(5)(7) – Developing renewable energy products enabled by
silicon-based nanomaterials
|
||||||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
16,666,666
|
5,718,216
|
||||||
|
Series
C Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
5,810,577
|
1,993,568
|
||||||
|
7,711,784
|
||||||||||
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED
SCHEDULE OF INVESTMENTS AS OF DECEMBER
31, 2007
|
|
Method
of
|
Shares/
|
|||||||||
|
Valuation
(1)
|
Principal
|
Value
|
||||||||
|
Investments
in Non-Controlled Affiliated Companies (2)(10) – 38.06% of net assets
at value (cont.)
|
||||||||||
|
Private
Placement Portfolio (Illiquid) – 38.06% of net assets at value
(cont.)
|
||||||||||
|
Kereos,
Inc. (4)(5)(7) — Developing emulsion-based imaging agents and targeted
therapeutics to image and treat cancer and cardiovascular
disease
|
||||||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
545,456
|
$
|
159,743
|
|||||
|
Kovio,
Inc. (4)(5)(7) — Developing semiconductor products using printed
electronics and thin-film technologies
|
||||||||||
|
Series
C Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
2,500,000
|
3,125,000
|
||||||
|
Series
D Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
800,000
|
1,000,000
|
||||||
|
4,125,000
|
||||||||||
|
Lifco,
Inc. (4)(5)(6)(7)(15) — Developing energy solutions using nanostructured
materials
|
||||||||||
|
Series
A Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
1,208,262
|
946,528
|
||||||
|
Mersana
Therapeutics, Inc. (4)(5)(7)(16) — Developing advanced polymers for drug
delivery
|
||||||||||
|
Series
A Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
68,451
|
136,902
|
||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
866,500
|
1,733,000
|
||||||
|
Warrants
at $2.00 expiring 10/21/10
|
(B)
|
|
91,625
|
118,380
|
||||||
|
|
1,988,282
|
|||||||||
|
Metabolon,
Inc. (4)(5)(7) – Discovering biomarkers through the use of
metabolomics
|
||||||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
2,173,913
|
2,500,000
|
||||||
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED
SCHEDULE OF INVESTMENTS AS OF DECEMBER
31, 2007
|
|
Method
of
|
Shares/
|
|||||||||
|
Valuation
(1)
|
Principal
|
Value
|
||||||||
|
Investments
in Non-Controlled Affiliated Companies (2)(10) – 38.06% of net assets
at value (cont.)
|
||||||||||
|
Private
Placement Portfolio (Illiquid) – 38.06% of net assets at value
(cont.)
|
||||||||||
|
NanoGram
Corporation (4)(5)(7) — Developing a broad suite of intellectual property
utilizing nanoscale materials
|
||||||||||
|
Series
I Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
63,210
|
$
|
124,524
|
|||||
|
Series
II Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
1,250,904
|
2,464,281
|
||||||
|
Series
III Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
1,242,144
|
2,447,024
|
||||||
|
Series
IV Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
432,179
|
851,393
|
||||||
|
5,887,222
|
||||||||||
|
Nanomix,
Inc. (4)(5)(7) — Producing nanoelectronic sensors that integrate carbon
nanotube electronics with silicon microstructures
|
||||||||||
|
Series
C Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
977,917
|
330,228
|
||||||
|
Series
D Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
6,802,397
|
680,240
|
||||||
|
1,010,468
|
||||||||||
|
NanoOpto
Corporation (4)(5)(17) — Manufactured discrete and integrated optical
communications sub-components on a chip by utilizing nano
manufacturing and nano coating technology
|
||||||||||
|
Series
A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
267,857
|
0
|
||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
3,819,935
|
0
|
||||||
|
Series
C Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
1,932,789
|
0
|
||||||
|
Series
D Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
1,397,218
|
0
|
||||||
|
Warrants
at $0.4359 expiring 03/15/10
|
(B)
|
|
193,279
|
0
|
||||||
|
Secured
Convertible Bridge Note (including interest)
|
(B)
|
|
$
|
268,654
|
105,714
|
|||||
|
|
105,714
|
|||||||||
|
Nextreme
Thermal Solutions, Inc. (4)(5)(7) — Developing thin-film thermoelectric
devices for cooling and energy conversion
|
||||||||||
|
Series
A Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
1,750,000
|
1,750,000
|
||||||
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED
SCHEDULE OF INVESTMENTS AS OF DECEMBER
31, 2007
|
|
Method
of
|
Shares/
|
|||||||||
|
Valuation
(1)
|
Principal
|
Value
|
||||||||
|
Investments
in Non-Controlled Affiliated Companies (2)(10) – 38.06% of net assets
at value (cont.)
|
||||||||||
|
Private
Placement Portfolio (Illiquid) – 38.06% of net assets at value
(cont.)
|
||||||||||
|
Questech
Corporation (4)(5) — Manufacturing and marketing proprietary metal and
stone decorative tiles
|
||||||||||
|
Common
Stock
|
(B)
|
|
655,454
|
$
|
589,259
|
|||||
|
Warrants
at $1.50 expiring 11/19/08
|
(B)
|
|
5,000
|
1,085
|
||||||
|
Warrants
at $1.50 expiring 11/19/09
|
(B)
|
|
5,000
|
1,910
|
||||||
|
592,254
|
||||||||||
|
Siluria
Technologies, Inc. (4)(5)(6)(7) – Developing new-generation
nanomaterials
|
||||||||||
|
Series
S-2 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
482,218
|
160,723
|
||||||
|
Solazyme,
Inc. (4)(5)(7) — Developing energy-harvesting machinery of photosynthetic
microbes to produce industrial and pharmaceutical
molecules
|
||||||||||
|
Series
A Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
988,204
|
997,691
|
||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
495,246
|
500,000
|
||||||
|
1,497,691
|
||||||||||
|
Xradia,
Inc. (4)(5) – Designing, manufacturing and selling ultra high
resolution 3D x-ray microscopes and fluorescence imaging
systems
|
||||||||||
|
Series
D Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
3,121,099
|
4,000,000
|
||||||
|
Zia
Laser, Inc. (4)(5)(18) — Developed quantum dot semiconductor
lasers
|
||||||||||
|
Series
C Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
1,500,000
|
21,329
|
||||||
|
Total
Non-Controlled Private Placement Portfolio (cost:
$54,306,393)
|
$
|
52,651,189
|
||||||||
|
Total
Investments in Non-Controlled Affiliated Companies (cost:
$54,306,393)
|
$
|
52,651,189
|
||||||||
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED
SCHEDULE OF INVESTMENTS AS OF DECEMBER
31, 2007
|
|
Method
of
|
Shares/
|
|||||||||
|
Valuation
(1)
|
Principal
|
Value
|
||||||||
|
Investments
in Controlled Affiliated Companies (2)(19) – 3.15% of net assets at
value
|
||||||||||
|
Private
Placement Portfolio (Illiquid) – 3.15% of net assets at
value
|
||||||||||
|
Evolved
Nanomaterial Sciences, Inc. (4)(5)(20) — Developed nanoscale-enhanced
approaches for the resolution of chiral molecules
|
||||||||||
|
Series
A Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
5,870,021
|
$
|
0
|
|||||
|
Phoenix
Molecular Corporation (4)(5)(6)(7) – Developing technology to enable
the separation of difficult-to-separate materials.
|
||||||||||
|
Common
Stock
|
(B)
|
|
1,000
|
10
|
||||||
|
Unsecured
Convertible Bridge Note (including interest)
|
(B)
|
|
$
|
50,000
|
50,733
|
|||||
|
|
50,743
|
|||||||||
|
SiOnyx,
Inc. (4)(5)(7) — Developing silicon-based optoelectronic products enabled
by its proprietary "Black Silicon"
|
||||||||||
|
Series
A Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
233,499
|
135,686
|
||||||
|
Series
A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
2,966,667
|
1,723,930
|
||||||
|
Series
A-2 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
4,207,537
|
2,445,000
|
||||||
|
4,304,616
|
||||||||||
|
Total
Controlled Private Placement Portfolio (cost:
$6,935,743)
|
$
|
4,355,359
|
||||||||
|
Total
Investments in Controlled Affiliated Companies (cost:
$6,935,743)
|
$
|
4,355,359
|
||||||||
|
Total
Private Placement Portfolio (cost: $82,677,528)
|
$
|
78,110,384
|
||||||||
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED
SCHEDULE OF INVESTMENTS AS OF DECEMBER
31, 2007
|
|
U.S.
Government and Agency Securities –43.50% of net assets at
value
|
||||||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Bill — due date 02/21/08
|
(J)
|
|
$
|
2,750,000
|
$
|
2,738,725
|
||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 02/15/08, coupon 3.375%
|
(H)
|
|
15,005,000
|
15,006,200
|
||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 05/15/08, coupon 3.75%
|
(H)
|
|
9,000,000
|
9,010,530
|
||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 09/15/08, coupon 3.125%
|
(H)
|
|
5,000,000
|
4,991,800
|
||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 01/15/09, coupon 3.25%
|
(H)
|
|
3,000,000
|
3,005,160
|
||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 02/15/09, coupon 4.50%
|
(H)
|
|
5,100,000
|
5,176,908
|
||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 04/15/09, coupon 3.125%
|
(H)
|
|
3,000,000
|
3,001,410
|
||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 07/15/09, coupon 3.625%
|
(H)
|
|
3,000,000
|
3,023,910
|
||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 10/15/09, coupon 3.375%
|
(H)
|
|
3,000,000
|
3,018,510
|
||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 01/15/10, coupon 3.625%
|
(H)
|
|
3,000,000
|
3,034,680
|
||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 04/15/10, coupon 4.00%
|
(H)
|
|
3,000,000
|
3,060,930
|
||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 07/15/10, coupon 3.875%
|
(H)
|
|
3,000,000
|
3,060,930
|
||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 10/15/10, coupon 4.25%
|
(H)
|
|
2,000,000
|
2,063,900
|
||||||
|
Total
Investments in U.S. Government and Agency Securities (cost:
$59,552,933)
|
$
|
60,193,593
|
||||||||
|
Total
Investments (cost: $142,230,461)
|
$
|
138,303,977
|
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED
SCHEDULE OF INVESTMENTS AS OF DECEMBER 31,
2007
|
|
(1)
|
See
Footnote to Consolidated Schedule of Investments on page 78 for a
description of the Valuation
Procedures.
|
|
(2)
|
Investments
in unaffiliated companies consist of investments in which we own
less than
five percent of the voting shares of the portfolio company. Investments
in
non-controlled affiliated companies consist of investments in which
we own
five percent or more, but less than 25 percent, of the voting shares
of
the portfolio company, or where we hold one or more seats on the
portfolio
company’s Board of Directors but do not control the company. Investments
in controlled affiliated companies consist of investments in which
we own
25 percent or more of the voting shares of the portfolio company
or
otherwise control the company.
|
|
(3)
|
The
aggregate cost for federal income tax purposes of investments in
unaffiliated companies is $21,435,392. The gross unrealized appreciation
based on the tax cost for these securities is $1,732,194. The gross
unrealized depreciation based on the tax cost for these securities
is
$2,063,750.
|
|
(4)
|
Legal
restrictions on sale of investment.
|
|
(5)
|
Represents
a non-income producing security. Equity investments that have not
paid
dividends within the last 12 months are considered to be non-income
producing.
|
|
(6)
|
Initial
investment was made during 2007.
|
|
(7)
|
These
investments are development stage companies. A development stage
company
is defined as a company that is devoting substantially all of its
efforts
to establishing a new business, and either it has not yet commenced
its
planned principal operations, or it has commenced such operations
but has
not realized significant revenue from
them.
|
|
(8)
|
With
our purchase of Series E Convertible Preferred Stock of BioVex, we
received a warrant to purchase a number of shares of common stock
of
BioVex as determined by dividing 624,999.99 by the price per share
at
which the common stock is offered and sold to the public in connection
with the initial public offering. The ability to exercise this
warrant is therefore contingent on BioVex completing successfully
an
initial public offering before the expiration date of the warrant
of
September 27, 2012. The exercise price of this warrant shall be 110
percent of the initial public offering
price.
|
|
(9)
|
Continuum
Photonics, Inc., merged with Polatis, Ltd., to form Polatis,
Inc.
|
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED
SCHEDULE OF INVESTMENTS AS OF DECEMBER
31, 2007
|
|
(10)
|
The
aggregate cost for federal income tax purposes of investments in
non-controlled affiliated companies is $54,306,393. The gross unrealized
appreciation based on the tax cost for these securities is $10,915,201.
The gross unrealized depreciation based on the tax cost for these
securities is $12,570,405.
|
|
(11)
|
BridgeLux,
Inc., was previously named eLite Optoelectronics,
Inc.
|
| (12) |
On
November 30, 2007, Chlorogen filed a Certificate of Dissolution with
the
state of Delaware.
|
|
(13)
|
With
our investment in a secured convertible bridge note issued by CSwitch,
we
received a warrant to purchase a number of shares of the class of
stock
sold in the next financing of CSwitch equal to $529,322.36, the principal
of the note, divided by the lowest price per share of the class of
stock
sold in the next financing of CSwitch. The ability to exercise this
warrant is therefore contingent on CSwitch completing successfully
a
subsequent round of financing. The warrant will expire five years
from the date of the close of the next round of financing. The cost
basis of this warrant is $529.32.
|
|
(14)
|
D-Wave
Systems, Inc., is located and is doing business primarily in Canada.
We
invested in D-Wave Systems, Inc., through D-Wave USA, a Delaware
company.
Our investment is denominated in Canadian dollars and is subject
to
foreign currency translation. See "Note 2. Summary of Significant
Accounting Policies."
|
| (15) |
On
February 28, 2008, Lifco, Inc., merged with CFX Battery, Inc., to
form CFX
Battery, Inc.
|
|
(16)
|
Mersana
Therapeutics, Inc., was previously named Nanopharma
Corp.
|
|
(17)
|
On
July 19, 2007, NanoOpto Corporation sold its assets to API Nanotronics,
Inc.
|
|
(18)
|
On
November 30, 2006, the assets of Zia Laser, Inc., were acquired by
Innolume, Inc.
|
|
(19)
|
The
aggregate cost for federal income tax purposes of investments in
controlled affiliated companies is $6,935,743. The gross unrealized
appreciation based on the tax cost for these securities is $219,616.
The
gross unrealized depreciation based on the tax cost for these securities
is $2,800,000.
|
|
(20)
|
On
September 30, 2007, Evolved Nanomaterial Sciences, Inc., filed for
Chapter
7 bankruptcy.
|
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED
SCHEDULE OF INVESTMENTS AS OF DECEMBER 31,
2006
|
|
Method
of
Valuation
(3)
|
Shares/
Principal
|
Value
|
||||||||
|
Investments
in Unaffiliated Companies (6)(7) – 15.61% of net
assets
|
||||||||||
|
Private
Placement Portfolio (Illiquid) – 15.61% of net
assets
|
||||||||||
|
AlphaSimplex
Group, LLC (2) — Investment management company headed by
|
||||||||||
|
Dr.
Andrew W. Lo, holder of the Harris & Harris Group Chair at MIT
Limited
Liability Company Interest
|
(B)
|
|
—
|
$
|
10,521
|
|||||
|
Exponential
Business Development Company (1)(2) —
|
||||||||||
|
Venture
capital partnership focused on early stage companies
Limited
Partnership Interest
|
(B)
|
|
—
|
0
|
||||||
|
Molecular
Imprints, Inc. (1)(2) — Manufacturing nanoimprint lithography capital
equipment
|
||||||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(A)
|
|
1,333,333
|
2,000,000
|
||||||
|
Series
C Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(A)
|
|
1,250,000
|
2,500,000
|
||||||
|
Warrants
at $2.00 expiring12/31/11
|
(B)
|
|
125,000
|
0
|
||||||
|
4,500,000
|
||||||||||
|
Nanosys,
Inc. (1)(2)(5) — Developing zero and one-dimensional inorganic
nanometer-scale materials for use in nanotechnology- enabled
systems
|
||||||||||
|
Series
C Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(C)
|
|
803,428
|
2,370,113
|
||||||
|
Series
D Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(C)
|
|
1,016,950
|
3,000,003
|
||||||
|
5,370,116
|
||||||||||
|
Nantero,
Inc. (1)(2)(5) — Developing a high-density, nonvolatile, random access
memory chip, enabled by carbon nanotubes
|
||||||||||
|
Series
A Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(C)
|
|
345,070
|
1,046,908
|
||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(C)
|
|
207,051
|
628,172
|
||||||
|
Series
C Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(C)
|
|
188,315
|
571,329
|
||||||
|
2,246,409
|
||||||||||
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED
SCHEDULE OF INVESTMENTS AS OF DECEMBER
31, 2006
|
|
Method
of
Valuation
(3)
|
Shares/
Principal
|
Value
|
||||||||
|
Investments
in Unaffiliated Companies (6)(7) – 15.61% of net assets
(cont.)
|
||||||||||
|
Private
Placement Portfolio (Illiquid) – 15.61% of net assets
(cont.)
|
||||||||||
|
NeoPhotonics
Corporation (1)(2) — Developing and manufacturing planar optical devices
and components
|
||||||||||
|
Common
Stock
|
(C)
|
|
716,195
|
$
|
133,141
|
|||||
|
Series
1 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(C)
|
|
1,831,256
|
1,831,256
|
||||||
|
Series
2 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(C)
|
|
741,898
|
741,898
|
||||||
|
Series
3 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(C)
|
|
2,750,000
|
2,750,000
|
||||||
|
Warrants
at $0.15 expiring 01/26/10
|
(C)
|
|
16,364
|
164
|
||||||
|
Warrants
at $0.15 expiring 12/05/10
|
(C)
|
|
14,063
|
140
|
||||||
|
5,456,599
|
||||||||||
|
Polatis,
Inc. (1)(2)(5)(10) — Developing optical networking components by merging
materials, MEMS and electronics technologies
|
||||||||||
|
Series
A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
16,775
|
0
|
||||||
|
Series
A-2 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
71,611
|
141,520
|
||||||
|
Series
A-4 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
4,774
|
9,435
|
||||||
|
Series
A-5 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
5,491
|
45,127
|
||||||
|
196,082
|
||||||||||
|
Total
Unaffiliated Private Placement Portfolio (cost:
$18,107,124)
|
$
|
17,779,727
|
||||||||
|
Total
Investments in Unaffiliated Companies (cost:
$18,107,124)
|
$
|
17,779,727
|
||||||||
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED
SCHEDULE OF INVESTMENTS AS OF DECEMBER
31, 2006
|
|
Method
of
Valuation
(3)
|
Shares/
Principal
|
Value
|
||||||||
|
Investments
in Non-Controlled Affiliated Companies (6)(8) – 28.20% of net
assets
|
||||||||||
|
Private
Placement Portfolio (Illiquid) – 28.20% of net
assets
|
||||||||||
|
BridgeLux,
Inc. (1)(2)(11) — Manufacturing high-power light emitting
diodes
|
||||||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(A)
|
|
1,861,504
|
$
|
1,000,000
|
|||||
|
Cambrios
Technologies Corporation (1)(2)(5) — Developing nanowire- enabled
electronic materials for the display industry
|
||||||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(A)
|
|
1,294,025
|
1,294,025
|
||||||
|
Chlorogen,
Inc. (1)(2)(5) — Developing patented chloroplast technology to produce
plant-made proteins
|
||||||||||
|
Series
A Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(C)
|
|
4,478,038
|
785,000
|
||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(C)
|
|
2,077,930
|
364,261
|
||||||
|
Secured
Convertible Bridge Note (including interest)
|
(A)
|
|
$
|
221,438
|
225,697
|
|||||
|
1,374,958
|
||||||||||
|
Crystal
IS, Inc. (1)(2)(5) — Developing single-crystal aluminum nitride substrates
for optoelectronic devices
|
||||||||||
|
Series
A Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(C)
|
|
|
391,571
|
|
|
305,425
|
|
||
|
Series
A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
|
|
(C)
|
|
1,300,376
|
1,014,294
|
||||
|
Warrants
at $0.78 expiring 05/05/2013
|
(B)
|
|
15,231
|
0
|
||||||
|
Warrants
at $0.78 expiring 05/12/2013
|
(B)
|
|
2,350
|
0
|
||||||
|
Warrants
at $0.78 expiring 08/08/2013
|
(B)
|
|
4,396
|
0
|
||||||
|
1,319,719
|
||||||||||
|
CSwitch,
Inc. (1)(2)(5) — Developing next-generation, system-on-a-chip solutions
for communications-based platforms
|
||||||||||
|
Series
A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(C)
|
|
6,700,000
|
3,350,000
|
||||||
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED
SCHEDULE OF INVESTMENTS AS OF DECEMBER
31, 2006
|
|
|
|
Method
of
Valuation
(3)
|
|
Shares/
Principal
|
|
Value
|
|
|||
|
Investments
in Non-Controlled Affiliated Companies (6)(8) – 28.20% of net assets
(cont.)
|
||||||||||
|
Private
Placement Portfolio (Illiquid) – 28.20% of net assets
(cont.)
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D-Wave
Systems, Inc. (1)(2)(4)(5)(13) — Developing high-performance quantum
computing systems
|
||||||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(A)
|
|
2,000,000
|
$
|
1,716,444
|
|||||
|
Warrants
at $0.85 expiring 10/19/07
|
(B)
|
|
1,800,000
|
0
|
||||||
|
1,716,444
|
||||||||||
|
Innovalight,
Inc. (1)(2)(4)(5) - Developing renewable energy products enabled
by
silicon-based nanomaterials
|
||||||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(A)
|
|
16,666,666
|
2,500,000
|
||||||
|
Kereos,
Inc. (1)(2)(5) — Developing emulsion-based imaging agents and targeted
therapeutics to image and treat cancer and cardiovascular
disease
|
||||||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(A)
|
|
349,092
|
960,000
|
||||||
|
Kovio,
Inc. (1)(2)(5) — Developing semiconductor products using printed
electronics and thin-film technologies
|
||||||||||
|
Series
C Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(A)
|
|
2,500,000
|
3,000,000
|
||||||
|
Mersana
Therapeutics, Inc. (1)(2)(5)(12) — Developing advanced polymers for drug
delivery
|
||||||||||
|
Series
A Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(C)
|
|
68,452
|
136,904
|
||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(C)
|
|
616,500
|
1,233,000
|
||||||
|
Warrants
at $2.00 expiring 10/21/10
|
(B)
|
|
91,625
|
0
|
||||||
|
1,369,904
|
||||||||||
|
Metabolon,
Inc. (1)(2)(4)(5) - Discovering biomarkers through the use of
metabolomics
|
||||||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(A)
|
|
2,173,913
|
2,500,000
|
||||||
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED
SCHEDULE OF INVESTMENTS AS OF DECEMBER
31, 2006
|
|
|
|
Method
of
Valuation
(3)
|
|
Shares/
Principal
|
|
Value
|
|
|||
|
Investments
in Non-Controlled Affiliated Companies (6)(8) – 28.20% of net assets
(cont.)
|
||||||||||
|
Private
Placement Portfolio (Illiquid) – 28.20% of net assets
(cont.)
|
||||||||||
|
NanoGram
Corporation (1)(2)(5) — Developing a broad suite of intellectual property
utilizing nanotechnology
|
||||||||||
|
Series
I Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(C)
|
|
63,210
|
$
|
64,259
|
|||||
|
Series
II Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(C)
|
|
1,250,904
|
1,271,670
|
||||||
|
Series
III Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(C)
|
|
1,242,144
|
1,262,764
|
||||||
|
|
2,598,693
|
|||||||||
|
Nanomix,
Inc. (1)(2)(5) — Producing nanoelectronic sensors that integrate carbon
nanotube electronics with silicon microstructures
|
||||||||||
|
Series
C Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
9,779,181
|
790,000
|
||||||
|
NanoOpto
Corporation (1)(2)(5) — Manufacturing discrete and integrated optical
communications sub-components on a chip by utilizing nano manufacturing
and nano coating technology
|
||||||||||
|
Series
A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
267,857
|
16,400
|
||||||
|
Series
B Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
3,819,935
|
560,328
|
||||||
|
Series
C Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
1,932,789
|
425,266
|
||||||
|
Series
D Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(B)
|
|
1,397,218
|
204,951
|
||||||
|
Warrants
at $0.4359 expiring 03/15/10
|
(B)
|
|
193,279
|
0
|
||||||
|
1,206,945
|
||||||||||
|
Nextreme
Thermal Solutions, Inc. (1)(2)(5) — Developing thin-film thermoelectric
devices
|
||||||||||
|
Series
A Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(A)
|
|
1,000,000
|
1,000,000
|
||||||
|
Questech
Corporation (1)(2) — Manufacturing and marketing proprietary metal and
stone decorative tiles
|
||||||||||
|
Common
Stock
|
(B)
|
|
655,454
|
996,683
|
||||||
|
Warrants
at $1.50 expiring 11/21/07
|
(B)
|
|
3,750
|
77
|
||||||
|
Warrants
at $1.50 expiring 11/19/08
|
(B)
|
|
5,000
|
103
|
||||||
|
Warrants
at $1.50 expiring 11/19/09
|
(B)
|
|
5,000
|
103
|
||||||
|
996,966
|
||||||||||
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED
SCHEDULE OF INVESTMENTS AS OF DECEMBER
31, 2006
|
|
|
|
Method
of
Valuation
(3)
|
|
Shares/
Principal
|
|
Value
|
|
|||
|
Investments
in Non-Controlled Affiliated Companies (6)(8) – 28.20% of net assets
(cont.)
|
||||||||||
|
Private
Placement Portfolio (Illiquid) – 28.20% of net assets
(cont.)
|
||||||||||
|
Solazyme,
Inc. (1)(2)(5) — Developing energy-harvesting machinery of photosynthetic
microbes to produce industrial and pharmaceutical
molecules
|
||||||||||
|
Series
A Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(C)
|
|
988,204
|
$
|
385,400
|
|||||
|
Starfire
Systems, Inc. (1)(2)(5) —Producing ceramic-forming
polymers
|
||||||||||
|
Common
Stock
|
(A)
|
|
375,000
|
150,000
|
||||||
|
Series
A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(C)
|
|
600,000
|
600,000
|
||||||
|
|
750,000
|
|||||||||
|
Xradia,
Inc. (1)(2)(4) - Designing, manufacturing and selling ultra high
resolution 3D x-ray microscopes and fluorescence imaging
systems.
|
||||||||||
|
Series
D Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(A)
|
|
3,121,099
|
4,000,000
|
||||||
|
Zia
Laser, Inc. (1)(2)(5) — Developing quantum dot semiconductor
lasers
|
||||||||||
|
Series
C Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(C)
|
|
1,500,000
|
15,000
|
||||||
|
Total
Non-Controlled Private Placement Portfolio (cost:
$39,571,676)
|
$
|
32,128,054
|
||||||||
|
Total
Investments in Non-Controlled Affiliated Companies (cost:
$39,571,676)
|
$
|
32,128,054
|
||||||||
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED
SCHEDULE OF INVESTMENTS AS OF DECEMBER 31,
2006
|
|
|
|
Method
of
Valuation
(3)
|
|
Shares/
Principal
|
|
Value
|
|
|||
|
Investments
in Controlled Affiliated Companies (6)(9) – 3.30% of net
assets
|
||||||||||
|
Private
Placement Portfolio (Illiquid) – 3.30% of net
assets
|
||||||||||
|
Evolved
Nanomaterial Sciences, Inc. (1)(2)(4)(5) — Developing
nanotechnology-enhanced approaches for the resolution of chiral
molecules
|
||||||||||
|
Series
A Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(A)
|
|
5,870,021
|
$
|
2,800,000
|
|||||
|
SiOnyx,
Inc. (1)(2)(4)(5) — Developing silicon-based optoelectronic products
enabled by its proprietary, "Black Silicon"
|
||||||||||
|
Series
A Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(C)
|
|
233,499
|
70,050
|
||||||
|
Series
A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock
|
(C)
|
|
2,966,667
|
890,000
|
||||||
|
960,050
|
||||||||||
|
Total
Controlled Private Placement Portfolio (cost:
$4,440,000)
|
$
|
3,760,050
|
||||||||
|
Total
Investments in Controlled Affiliated Companies (cost:
$4,440,000)
|
$
|
3,760,050
|
||||||||
|
U.S.
Government and Agency Securities – 51.48% of net
assets
|
||||||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Bill — due date 1/18/07
|
(J)
|
|
2,217,000
|
2,212,677
|
||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 11/30/07, coupon 4.25%
|
(H)
|
|
6,500,000
|
6,455,345
|
||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 02/15/08, coupon 3.375%
|
(H)
|
|
9,000,000
|
8,842,860
|
||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 05/15/08, coupon 3.75%
|
(H)
|
|
9,000,000
|
8,862,210
|
||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 09/15/08, coupon 3.125%
|
(H)
|
|
5,000,000
|
4,861,350
|
||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 01/15/09, coupon 3.25%
|
(H)
|
|
3,000,000
|
2,910,930
|
||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 02/15/09, coupon 4.50%
|
(H)
|
|
5,100,000
|
5,069,145
|
||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 04/15/09, coupon 3.125%
|
(H)
|
|
3,000,000
|
2,893,830
|
||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 07/15/09, coupon 3.625%
|
(H)
|
|
3,000,000
|
2,920,890
|
||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 10/15/09, coupon 3.375%
|
(H)
|
|
3,000,000
|
2,894,310
|
||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 01/15/10, coupon 3.625%
|
(H)
|
|
3,000,000
|
2,907,420
|
||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 04/15/10, coupon 4.00%
|
(H)
|
|
3,000,000
|
2,935,560
|
||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 07/15/10, coupon 3.875%
|
(H)
|
|
3,000,000
|
2,920,560
|
||||||
|
U.S.
Treasury Notes — due date 10/15/10, coupon 4.25%
|
(H)
|
|
2,000,000
|
1,969,060
|
||||||
|
Total
Investments in U.S. Government and Agency Securities (cost:
$59,212,598)
|
$
|
58,656,147
|
||||||||
|
Total
Investments (cost: $121,331,398)
|
$
|
112,323,978
|
||||||||
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
CONSOLIDATED
SCHEDULE OF INVESTMENTS AS OF DECEMBER 31,
2006
|
|
(1)
|
Represents
a non-income producing security. Equity investments that have not
paid
dividends within the last 12 months are considered to be non-income
producing.
|
|
(2)
|
Legal
restrictions on sale of investment.
|
|
(3)
|
See
Footnote to Schedule of Investments for a description of the Valuation
Procedures.
|
|
(4)
|
Initial
investment was made during 2006.
|
|
(5)
|
These
investments are development stage companies. A development stage
company
is defined as a company that is devoting substantially all of its
efforts
to establishing a new business, and either it has not yet commenced
its
planned principal operations, or it has commenced such operations
but has
not realized significant revenue from
them.
|
|
(6)
|
Investments
in unaffiliated companies consist of investments in which we own
less than
five percent of the voting shares of the portfolio company. Investments
in
non-controlled affiliated companies consist of investments in which
we own
five percent or more, but less than 25 percent, of the voting shares
of
the portfolio company or where we hold one or more seats on the portfolio
company’s Board of Directors. Investments in controlled affiliated
companies consist of investments in which we own 25 percent or more
of the
voting shares of the portfolio
company.
|
|
(7)
|
The
aggregate cost for federal income tax purposes of investments in
unaffiliated companies is $18,107,124. The gross unrealized appreciation
based on the tax cost for these securities is $1,732,194. The gross
unrealized depreciation based on the tax cost for these securities
is
$2,059,591.
|
|
(8)
|
The
aggregate cost for federal income tax purposes of investments in
non-controlled affiliated companies is $39,571,676. The gross unrealized
appreciation based on the tax cost for these securities is $333,269.
The
gross unrealized depreciation based on the tax cost for these securities
is $7,776,891.
|
|
(9)
|
The
aggregate cost for federal income tax purposes of investments in
controlled affiliated companies is $4,400,000. The gross unrealized
appreciation based on the tax cost for these securities is $0. The
gross
unrealized depreciation based on the tax cost for these securities
is
$679,950.
|
|
(10)
|
Continuum
Photonics, Inc., merged with Polatis, Ltd., to form Polatis,
Inc.
|
|
(11)
|
BridgeLux,
Inc., was previously named eLite Optoelectronics,
Inc.
|
|
(12)
|
Mersana
Therapeutics, Inc., was previously named Nanopharma
Corp.
|
|
(13)
|
D-Wave
Systems, Inc., is located and is doing business primarily in Canada.
We
invested in D-Wave Systems, Inc., through D-Wave USA, a Delaware
company.
Our investment is denominated in Canadian dollars and is subject
to
foreign currency translation. Refer to “Note 2. Summary of Significant
Accounting Policies.”
|
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
FOOTNOTE
TO CONSOLIDATED SCHEDULE OF
INVESTMENTS
|
|
·
|
The
cost of the Company’s investment;
|
|
·
|
Transactions
in a company's securities or unconditional firm offers by responsible
parties as a factor in determining
valuation;
|
| · |
The
financial condition and operating results of the
company;
|
| · |
The
long-term potential of the business and technology of the
company;
|
| · |
The
values of similar securities issued by companies in similar
businesses;
|
| · |
Multiples
to revenue, net income or EBITDA that similar securities issued by
companies in similar businesses receive;
|
| · |
The
proportion of the company's securities we own and the nature of any
rights
to require the company to register restricted securities under applicable
securities laws; and
|
| · |
The
rights and preferences of the class of securities we own as compared
to
other classes of securities the portfolio company has issued.
|
|
·
|
The
cost of the investment;
|
|
·
|
Investments
in the same or substantially similar intellectual property or patents
or
research and development in technology or product development or
offers by
responsible third parties;
|
|
·
|
The
results of research and
development;
|
|
·
|
Product
development progress;
|
|
·
|
Commercial
prospects;
|
|
·
|
Term
of patent;
|
|
·
|
Projected
markets; and
|
|
·
|
Other
subjective factors.
|
|
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL
STATEMENTS
|
|
December
31, 2007
|
||||||||||
|
Geographic Region
|
Fair Value
|
Percentage of
Total Private
Placement
Portfolio
|
Percentage
of Net Assets
|
|||||||
|
West
|
$
|
50,124,606
|
64.2
|
%
|
36.2
|
%
|
||||
|
Northeast
|
$
|
16,849,547
|
21.6
|
%
|
12.2
|
%
|
||||
|
Midwest
|
$
|
4,659,743
|
6.0
|
%
|
3.4
|
%
|
||||
|
Southeast
|
$
|
4,250,000
|
5.4
|
%
|
3.1
|
%
|
||||
|
Outside
U.S.
|
$
|
2,226,488
|
2.8
|
%
|
1.6
|
%
|
||||
|
$
|
78,110,384
|
100.0
|
%
|
|||||||
|
December
31, 2006
|
||||||||||
|
Geographic
Region
|
Fair Value
|
Percentage of
Total Private
Placement
Portfolio
|
Percentage
of Net Assets
|
|||||||
|
West
|
$
|
29,759,833
|
55.5
|
%
|
26.1
|
%
|
||||
|
Northeast
|
$
|
11,856,596
|
22.1
|
%
|
10.4
|
%
|
||||
|
Midwest
|
$
|
6,834,958
|
12.7
|
%
|
6.0
|
%
|
||||
|
Southeast
|
$
|
3,500,000
|
6.5
|
%
|
3.1
|
%
|
||||
|
Outside
U.S.
|
$
|
1,716,444
|
3.2
|
%
|
1.5
|
%
|
||||
|
$
|
53,667,831
|
100.0
|
%
|
|||||||
|
Type of Award
|
|
Term
|
|
Number
of Options
Granted
|
|
Expected
Term
in Yrs
|
|
Expected
Volatility
Factor
|
|
Expected
Dividend
Yield
|
|
Risk-free
Interest
Rates
|
|
Weighted
Average
Fair
Value
Per Share
|
||||||||
|
Non-qualified
stock options
|
1 Year
|
1,001,017
|
0.75
|
37.4%
|
|
0%
|
|
5.16%
|
|
$
|
1.48
|
|||||||||||
|
Non-qualified
stock options
|
2 Years
|
815,000
|
1.625
|
45.2%
|
0%
|
|
5.12%
|
|
$
|
2.63
|
||||||||||||
|
Non-qualified
stock options
|
3 Years
|
659,460
|
2.42
|
55.7%
|
|
0%
|
|
5.09%
|
|
$
|
3.81
|
|||||||||||
|
Non-qualified
stock options
|
10 Years
|
|
690,000
|
5.75
|
75.6%
|
|
0%
|
|
5.08%
|
|
$
|
6.94
|
||||||||||
|
Incentive
stock options
|
10 Years
|
792,806
|
7.03
|
75.6%
|
|
0%
|
|
5.08%
|
|
$
|
7.46
|
|||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Total
|
3,958,283
|
$
|
4.25
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Type
of Award
|
Contractual
Term
|
Number
of Options
Granted
|
Expected
Term
in Yrs
|
Expected
Volatility
Factor
|
Expected
Dividend
Yield
|
Risk-free
Interest
Rates
|
Fair
Value
Per Share
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Non-qualified
stock options
|
1.5
Years
|
380,000
|
1
|
42.6%
|
|
0%
|
|
4.93%
|
|
$
|
2.11
|
|||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Non-qualified
stock options
|
2.5
Years
|
600,540
|
2
|
40.1%
|
|
0%
|
|
4.91%
|
|
$
|
2.92
|
|||||||||||
|
Non-qualified
stock options
|
3.5
Years
|
338,403
|
3
|
44.7%
|
|
0%
|
|
4.93%
|
|
$
|
3.94
|
|||||||||||
|
Non-qualified
stock options
|
9
Years
|
381,666
|
Ranging
from 4.75- 6.28
|
Ranging
from 57.8% to 59.9%
|
|
0%
|
|
Ranging
from 4.97% to 5.01%
|
|
Ranging
from $5.92 to $6.85
|
||||||||||||
|
Total
|
1,700,609
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Shares
|
|
Weighted
Average
Exercise
Price
|
|
Weighted
Average
Grant Date
Fair Value
|
|
Weighted
Average
Remaining
Contractual
Term (Yrs)
|
|
Aggregate
Intrinsic
Value
|
||||||||
|
Options
Outstanding at December
31, 2006
|
3,699,611
|
$
|
10.11
|
$
|
4.43
|
|||||||||||
|
Granted
|
1,700,609
|
$
|
11.11
|
$
|
3.68
|
3.43
|
||||||||||
|
Exercised
|
(999,556
|
)
|
$
|
10.11
|
$
|
1.97
|
||||||||||
|
Forfeited
or Expired
|
(432,920
|
)
|
$
|
3.99
|
||||||||||||
|
Options
Outstanding at December
31, 2007
|
3,967,744
|
$
|
10.54
|
$
|
4.77
|
4.58
|
$
|
0
|
||||||||
|
Options
Exercisable at December
31, 2007
|
1,717,125
|
$
|
10.43
|
$
|
4.45
|
4.18
|
$
|
0
|
||||||||
|
Options
Exercisable and Expected to be Exercisable
at December 31, 2007
|
3,858,226
|
$
|
10.55
|
$
|
4.70
|
4.47
|
$
|
0
|
||||||||
|
2007
|
|
2006
|
|||||
|
Accumulated
Postretirement Benefit Obligation at Beginning of Year
|
$
|
696,827
|
$
|
675,334
|
|||
|
Service
Cost
|
102,676
|
79,381
|
|||||
|
Interest
Cost
|
33,935
|
33,786
|
|||||
|
Actuarial
(Gain)/Loss
|
(196,248
|
)
|
(84,879
|
)
|
|||
|
Benefits
Paid
|
(8,445
|
)
|
(6,795
|
)
|
|||
|
Accumulated
Postretirement Benefit Obligation at End of Year
|
$
|
628,745
|
$
|
696,827
|
|||
|
1% Decrease
in Rates
|
Assumed
Rates
|
1% Increase
in Rates
|
||||||||
|
Aggregated
Service and Interest Cost
|
$
|
105,317
|
$
|
136,611
|
$
|
179,692
|
||||
|
Accumulated
Postretirement Benefit Obligation
|
$
|
606,717
|
$
|
628,745
|
$
|
883,758
|
||||
|
2007
|
|
2006
|
|
2005
|
||||||
|
Service
Cost
|
$
|
102,676
|
$
|
79,381
|
$
|
49,990
|
||||
|
Interest
Cost on Accumulated Postretirement Benefit Obligation
|
33,935
|
33,786
|
32,573
|
|||||||
|
Amortization
of Transition Obligation
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|||||||
|
Amortization
of Net (Gain)/Loss
|
(6,234
|
)
|
0
|
0
|
||||||
|
Net
Periodic Post Retirement Benefit Cost
|
$
|
130,377
|
$
|
113,167
|
$
|
82,563
|
||||
|
2008
|
$
|
18,489
|
||
|
2009
|
$
|
23,639
|
||
|
2010
|
$
|
25,584
|
||
|
2011
|
$
|
20,213
|
||
|
2012
|
$
|
21,663
|
||
|
2013
through 2017
|
$
|
135,078
|
|
|
2007
|
2006
|
2005
|
|||||||
|
Investment
operations
|
$
|
0
|
$
|
0
|
$
|
0
|
||||
|
Realized
income on investments
|
87,975
|
(227,355
|
)
|
1,530,881
|
||||||
|
Taxes
paid on behalf of shareholders
|
0
|
0
|
8,122,367
|
|||||||
|
Increase
(decrease) in unrealized appreciation on investments
|
0
|
(0
|
)
|
(1,364,470
|
)
|
|||||
|
Total
income tax (benefit) expense
|
$
|
87,975
|
$
|
(227,355
|
)
|
$
|
8,288,778
|
|||
|
2007
|
2006
|
2005
|
||||||||
|
Current
|
$
|
87,975
|
$
|
(227,355
|
)
|
$
|
9,653,248
|
|||
|
Deferred —
Federal
|
0
|
0
|
(1,364,470
|
)
|
||||||
|
Total
income tax (benefit) expense
|
$
|
87,975
|
$
|
(227,355
|
)
|
$
|
8,288,778
|
|||
|
2007
|
2006
|
2005
|
||||||||
|
Numerator
for (decrease) increase in net assets per share
|
$
|
(6,716,445
|
)
|
$
|
(11,773,112
|
)
|
$
|
6,716,376
|
||
|
Denominator
for basic and diluted weighted average shares
|
22,393,030
|
20,759,547
|
18,471,770
|
|||||||
|
Basic
and diluted net (decrease) increase in net assets per share resulting
from
operations
|
$
|
(0.30
|
)
|
$
|
(0.57
|
)
|
$
|
0.36
|
||
|
2007
|
|||||||||||||
|
1st Quarter
|
2nd Quarter
|
3rd Quarter
|
4th Quarter
|
||||||||||
|
Total
investment income
|
$
|
652,498
|
$
|
637,701
|
$
|
743,414
|
$
|
672,023
|
|||||
|
Net
operating loss
|
$
|
(2,667,118
|
)
|
$
|
(2,891,667
|
)
|
$
|
(3,117,595
|
)
|
$
|
(3,151,163
|
)
|
|
|
Net
increase (decrease) in net assets resulting from
operations
|
$
|
(6,390,160
|
)
|
$
|
(4,093,644
|
)
|
$
|
604,237
|
$
|
3,163,122
|
|||
|
Net
(decrease) increase in net assets resulting from operations per
average
outstanding share
|
$
|
(0.30
|
)
|
$
|
(0.19
|
)
|
$
|
0.03
|
$
|
0.16
|
|||
|
2006
|
|||||||||||||
|
1st Quarter
|
|
2nd Quarter
|
|
3rd Quarter
|
|
4th Quarter
|
|||||||
|
Total
investment income
|
$
|
804,862
|
$
|
785,265
|
$
|
719,619
|
$
|
719,015
|
|||||
|
Net
operating loss
|
$
|
(767,743
|
)
|
$
|
(693,887
|
)
|
$
|
(2,988,790
|
)
|
$
|
(3,162,515
|
)
|
|
|
Net
increase (decrease) in net assets resulting from
operations
|
$
|
(1,653,990
|
)
|
$
|
(1,282,997
|
)
|
$
|
(2,588,092
|
)
|
$
|
(6,248,033
|
)
|
|
|
Net
(decrease) increase in net assets resulting from operations per
average
outstanding share
|
$
|
(0.08
|
)
|
$
|
(0.06
|
)
|
$
|
(0.12
|
)
|
$
|
(0.31
|
)
|
|
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
FINANCIAL
HIGHLIGHTS
|
|
Year Ended
December 31, 2007
|
|
Year Ended
December 31, 2006
|
|
Year Ended
December 31, 2005
|
||||||
|
Per
Share Operating Performance
|
||||||||||
|
Net
asset value per share, beginning of year
|
$
|
5.42
|
$
|
5.68
|
$
|
4.33
|
||||
|
Net
operating (loss) income*
|
(0.53
|
)
|
(0.37
|
)
|
(0.30
|
)
|
||||
|
Net
realized income on investments*
|
0.00
|
0.01
|
0.77
|
|||||||
|
Net
increase (decrease) in unrealized appreciation (depreciation) as
a result
of sales*
|
0.00
|
0.00
|
(1.18
|
)
|
||||||
|
Net
increase (decrease) in unrealized appreciation (depreciation) on
investments held*
|
0.23
|
(0.21
|
)
|
1.07
|
||||||
|
Total
from investment operations*
|
(0.30
|
)
|
(0.57
|
)
|
0.36
|
|||||
|
Net
increase as a result of stock- based compensation expense*
|
0.36
|
0.24
|
0.00
|
|||||||
|
Net
increase as a result of proceeds from exercise of options
|
0.19
|
0.07
|
0.00
|
|||||||
|
Net
increase as a result of stock offering
|
0.26
|
0.00
|
0.99
|
|||||||
|
Total
increase from capital stock transactions
|
0.81
|
0.31
|
0.99
|
|||||||
|
Net
asset value per share, end of year
|
$
|
5.93
|
$
|
5.42
|
$
|
5.68
|
||||
|
Stock
price per share, end of year
|
$
|
8.79
|
$
|
12.09
|
$
|
13.90
|
||||
|
Total
return based on stock price
|
(27.3
|
)%
|
(13.0
|
)%
|
(15.1
|
)%
|
||||
|
Supplemental
Data:
|
||||||||||
|
Net
assets, end of year
|
$
|
138,363,344
|
$
|
113,930,303
|
$
|
117,987,742
|
||||
|
Ratio
of expenses to average net assets
|
11.6
|
%
|
9.2
|
%
|
7.5
|
%
|
||||
|
Ratio
of net operating loss to average net assets
|
(9.5
|
)%
|
(6.6
|
)%
|
(5.8
|
)%
|
||||
|
Cash
dividends paid per share
|
$
|
0.00
|
$
|
0.00
|
$
|
0.00
|
||||
|
Taxes
payable on behalf of shareholders on the deemed dividend per
share
|
$
|
0.00
|
$
|
0.00
|
$
|
0.39
|
||||
|
Number
of shares outstanding, end of year
|
23,314,573
|
21,015,017
|
20,756,345
|
|||||||
| (a) |
The
following documents are filed as a part of this
report:
|
| (1) |
Listed
below are the financial statements which are filed as part of this
report:
|
| · |
Consolidated
Statements of Assets and Liabilities as of December 31, 2007, and
2006;
|
| · |
Consolidated
Statements of Operations for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006,
and
2005;
|
| · |
Consolidated
Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006,
and
2005;
|
| · |
Consolidated
Statements of Changes in Net Assets for the years ended December
31, 2007,
2006, and 2005;
|
| · |
Consolidated
Schedule of Investments as of December 31,
2007;
|
| · |
Consolidated
Schedule of Investments as of December 31,
2006;
|
| · |
Footnote
to Consolidated Schedule of
Investments;
|
| · |
Notes
to Consolidated Financial Statements;
and
|
|
·
|
Financial
Highlights for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006, and
2005.
|
|
(2)
|
No
financial statement schedules are required to be filed herewith because
(i) such schedules are not required or (ii) the information has been
presented in the above financial
statements.
|
|
(3)
|
The
following exhibits are filed with this report or are incorporated
herein
by reference to a prior filing, in accordance with Rule 12b-32 under
the
Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
|
|
3.1(a)
|
Restated
Certificate of Incorporation of Harris & Harris Group, Inc., dated
September 23, 2005, incorporated by reference as Exhibit 99 to Form
8-K
(File No. 814-00176) filed on September 27,
2005.
|
|
3.1(b)
|
Certificate
of Amendment of the Certificate of Incorporation of Harris & Harris
Group, Inc., dated May 19, 2006, incorporated by reference as Exhibit
3.1
to the Company's Form 10-Q (File No. 814-00176) filed on August 9,
2006.
|
|
3.2
|
Restated
By-laws, incorporated by reference as Exhibit B to Pre-Effective
Amendment
No.1 to the Company's Registration Statement on Form N-2 (File No.
333-112862) filed on March 22,
2004.
|
|
4.1
|
Form
of Specimen Certificate of Common Stock, incorporated by reference
to
Exhibit D to the Company's Registration Statement on Form N-2 (File
No.
333-138996) filed November 29,
2006.
|
|
10.1
|
Harris
& Harris Group, Inc. Custodian Agreement with JP Morgan, incorporated
by reference as Exhibit J to Pre-Effective Amendment No. 1 to the
Company's Registration Statement on Form N-2 (File No. 333-112862)
filed
on March 22, 2004.
|
|
10.2
|
Form
of Indemnification Agreement which has been established with all
directors
and executive officers of the Company, incorporated by reference
as
Exhibit I(7) to Pre-Effective Amendment No. 1 to the Company's
Registration Statement on Form N-2 (File No. 333-112862) filed on
March
22, 2004.
|
|
10.3
|
Deferred
Compensation Agreement, incorporated by reference as Exhibit 10.5
to the
Company's Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2004 (File No.
814-00176) filed on March 16, 2005.
|
|
10.4
|
Amendment
No. 4 to Deferred Compensation Agreement, incorporated by reference
as
Exhibit 10 to the Company's Form 10-Q (File No. 814-00176) filed
on August
9, 2006.
|
|
10.5
|
Amendment
No. 2 to Deferred Compensation Agreement, incorporated by reference
as
Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Form 8-K (File No. 814-00176) filed
on
October 15, 2004.
|
|
10.6
|
Amendment
No. 1 to Deferred Compensation Agreement, incorporated by reference
as
Exhibit 10.2 to the Company's Form 10-Q (File No. 811-07074) filed
on May
14, 2003.
|
|
10.7
|
Trust
Under Harris & Harris Group, Inc., Deferred Compensation Agreement,
incorporated by reference as Exhibit I(12) to the Company's Registration
Statement on Form N-2 (File No. 333-138996) filed on November 29,
2006.
|
|
10.8*
|
Harris
& Harris Group, Inc. Amended and Restated Employee Profit-Sharing
Plan.
|
|
10.9
|
Harris
& Harris Group, Inc. 2006 Equity Incentive Plan, incorporated by
reference as Appendix B to the Company's Proxy Statement for the
2006
Annual Meeting of Shareholders filed on April 3,
2006.
|
| 10.10 |
Form
of Incentive Stock Option Agreement incorporated by reference as
Exhibit
10.1 to the Company's Form 8-K (File
No. 814-00176) filed
on June 26, 2006.
|
| 10.11 |
Form
of Non-Qualified Stock Option Agreement, incorporated by reference
as
Exhibit 10.2 to the Company's Form 8-K (File
No. 814-00176) filed
on June 26, 2006.
|
|
10.12
|
Harris
& Harris Group, Inc. Directors Stock Purchase Plan 2001, incorporated
by reference as Exhibit I(6) to the Company's Registration Statement
on
Form N-2 (File No. 333-138996) filed on November 29,
2006.
|
|
10.13
|
Amended
and Restated Employment Agreement between Harris & Harris Group, Inc.
and Charles E. Harris, dated August 2, 2007, incorporated by reference
as
Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Form 8-K (File No. 814-00176) filed on
August 3, 2007.
|
|
10.14
|
Amended
and Restated Severance Compensation Agreement, dated August 2, 2007,
incorporated by reference as Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Form 8-K (File
No. 814-00176) filed on August 3,
2007.
|
|
10.15
|
Amended
and Restated Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan, dated August
2, 2007,
incorporated by reference as Exhibit 10.3 to the Company’s Form 8-K (File
No. 814-00176) filed on August 3,
2007.
|
|
10.16
|
Amended
and Restated Harris & Harris Group, Inc. Executive Mandatory
Retirement Benefit Plan, dated August 2, 2007, incorporated by reference
as Exhibit 10.4 to the Company’s Form 8-K (File No. 814-00176) filed on
August 3, 2007.
|
|
10.17*
|
Agreement
of Sub-Sublease, dated April 18, 2003, by and between Prominent USA,
Inc.
and Harris & Harris Group, Inc.
|
|
10.18*
|
Amendment
to Agreement of Sub-Sublease, dated May 9, 2003, by and between Prominent
USA, Inc., and Harris & Harris Group,
Inc.
|
|
10.19*
|
Assignment
and Assumption, Modification and Extension of Sublease Agreement,
dated
December 17, 2004, by and among the Economist Newspaper Group, Inc.,
National Academy of Television Arts & Sciences, and Harris &
Harris Group, Inc.
|
|
14.1
|
Code
of Conduct for Directors and Employees of Harris & Harris Group, Inc.
incorporated by reference as Exhibit 14 to the Company's Form 8-K
(File
No. 814-00176) filed on October 5,
2004.
|
|
14.2
|
Code
of Ethics Pursuant to Rule 17j-1, incorporated by reference as Exhibit
14
to the Company's Form 8-K (File No. 814-00176) filed on March 7,
2008.
|
|
31.01*
|
Certification
of CEO pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of
2002.
|
|
31.02*
|
Certification
of CFO pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of
2002.
|
|
32.01*
|
Certification
of CEO and CFO pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant
to
Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of
2002.
|
|
HARRIS
& HARRIS GROUP, INC.
|
||
|
Date:
March 12, 2008
|
By:
|
/s/
Charles E. Harris
|
|
Charles
E. Harris
|
||
|
Chairman
of the Board
|
||
|
Signatures
|
Title
|
Date
|
||
|
/s/
Charles E. Harris
|
Chairman
of the Board
|
March
12, 2008
|
||
|
Charles
E. Harris
|
and
Chief Executive Officer
|
|||
|
/s/
Daniel B. Wolfe
|
Chief
Financial Officer
|
March
12, 2008
|
||
|
Daniel
B. Wolfe
|
||||
|
/s/
Patricia N. Egan
|
Chief
Accounting Officer
|
March
12, 2008
|
||
| Patricia N. Egan |
and
Senior Controller
|
|
||
|
/s/
W. Dillaway Ayres, Jr.
|
Director
|
March
12, 2008
|
||
|
W.
Dillaway Ayres, Jr.
|
||||
|
/s/
C. Wayne Bardin
|
Director
|
March
12, 2008
|
||
|
C.
Wayne Bardin
|
|
/s/
Phillip A. Bauman
|
Director
|
March
12, 2008
|
||
|
Phillip
A. Bauman
|
||||
|
/s/
G. Morgan Browne
|
Director
|
March
12, 2008
|
||
|
G.
Morgan Browne
|
||||
|
/s/
Dugald A. Fletcher
|
Director
|
March
12, 2008
|
||
|
Dugald
A. Fletcher
|
||||
|
/s/
Douglas W. Jamison
|
Director
|
March
12, 2008
|
||
|
Douglas
W. Jamison
|
||||
|
/s/
Kelly S. Kirkpatrick
|
Director
|
March
12, 2008
|
||
|
Kelly
S. Kirkpatrick
|
||||
|
/s/
Lori D. Pressman
|
Director
|
March
12, 2008
|
||
|
Lori
D. Pressman
|
||||
|
/s/
Charles E. Ramsey
|
Director
|
March
12, 2008
|
||
|
Charles
E. Ramsey
|
||||
|
/s/
James E. Roberts
|
Director
|
March
12, 2008
|
||
|
James
E. Roberts
|
||||
|
/s/
Richard P. Shanley
|
Director
|
March
12, 2008
|
||
|
Richard
P. Shanley
|
|
Description
|
||
|
10.8
|
Harris
& Harris Group, Inc. Amended and Restated Employee Profit-Sharing
Plan.
|
|
|
10.17
|
Agreement
of Sub-Sublease, dated April 18, 2003, by and between Prominent USA,
Inc.
and Harris & Harris Group, Inc.
|
|
|
10.18
|
Amendment
to Agreement of Sub-Sublease, dated May 9, 2003, by and between Prominent
USA, Inc., and Harris & Harris Group, Inc.
|
|
|
10.19
|
Assignment
and Assumption, Modification and Extension of Sublease Agreement,
dated
December 17, 2004, by and among the Economist Newspaper Group, Inc.,
National Academy of Television Arts & Sciences, and Harris &
Harris Group, Inc.
|
|
|
31.01
|
Certification
of CEO pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of
2002.
|
|
|
31.02
|
Certification
of CFO pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of
2002.
|
|
|
32.01
|
Certification
of CEO and CFO pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant
to
Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of
2002.
|